Documentation of the Alter-Java GUI
This documentation illustrates the functionality of the graphical user interface, which has been implemented to illustrate an algorithm from the Alter-Java framework. The GUI is adaptable for every kind of algorithm, which is implemented in the Alter-Java framework. The following guide illustrates, how the graphical user interface can be used.
Design and building
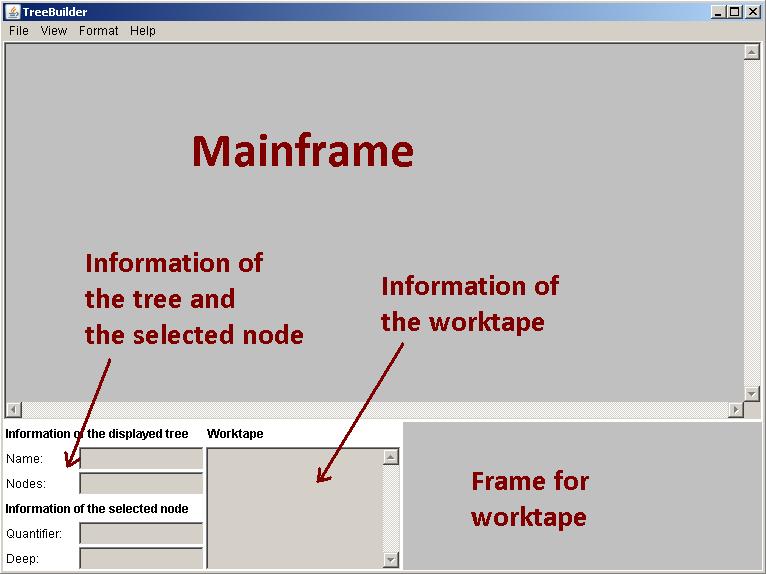
The graphical user interface consists of following components:
- Mainframe
- Information-panels for the tree and a selected node
- Information-panel for the work variables of the current node
- Frame to illustrate a node graphically
Menu
The menu of the GUI offers the possibility to edit the view of the computation tree. It offers the following menu-points:
- File
- Exit
Closes the program with all it's components.
- Exit
- View
- Tree-View
Changes the view to the tree-presentation. If the tree-view is already in use, this menu-point is not available. - List-View
Changes the view to the list-presentation. If the list-view is already in use, this menu-point is not available.
- Tree-View
- Format
- Tree-Format
Opens a panel, where the dimensions of the nodes and the space between the nodes can be edit. - Minimize
Minimize the whole tree, so that all nodes of the tree don't show their children. Because of that only the root-node is visible. - Maximize
Maximize the tree up to a defined depth. It opens a panel, where the user can give the maximum depth, the tree should be shown. All nodes, which are higher or in the same depth, will be shown. - Positive Ways
Minimize all nodes, which illustrates a negative way of the tree. All nodes, which are positive are shown. If a positive node is under a negative node, this postive node won't be shown.
- Tree-Format
- Help
- Info
Gives information about the program and it's authors.
- Info
Usage of the GUI - Code Implementation
The Implementation of the worktape in the graphical user interface needs a few components, which has to be down by the developer of an Alter-Java program. The GUI offers the class DefaultFormat, with the necessary methods, which can be extended.
The class DefaultFormat in the Package at.ac.tuwien.dbai.alternation.gui contains the following
methods:
If an own class is defined and extends the DefaultFormat-class,
this class should be instantiated. The Object of this class offers the
method setFormat, where the Dimension of the nodes and the
space between the nodes can be defined. Without using this method the
class defines default parameters for the application.
To create a mainframe of the GUI, it is necessary to instantiate
the class Mainframe of the package at.ac.tuwien.dbai.alternation.gui.
The constructor of the class needs the computation-tree of the
alternation-example, the own implemented class which extends DefaultFormat
and an integer-value, which defines the maximum tree deep, to which the gets
drawn. (Please mention that the computation tree may increase expontentially with the tree deep and thus for high deep the GUI may exeed the available resources of the java proccess)
For detailed information about the code-implementation have a look at the API of the application.
Examples
Maybe the best way to see how this GUI can be used is to study some examples:-
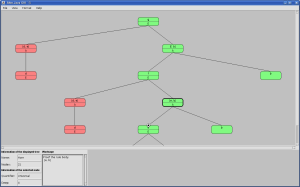 Horn: Alter-Java program - format-class
Horn: Alter-Java program - format-class 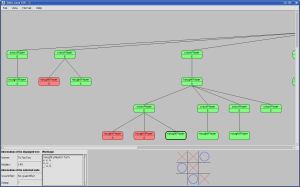 TicTacToe: Alter-Java program -format-class
TicTacToe: Alter-Java program -format-class 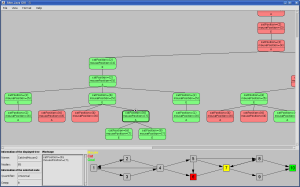 CatAndMouse:Alter-Java program - format-class
CatAndMouse:Alter-Java program - format-class
